Demystifying the Data Science Roles

Data Scientist vs Data Engineer: What’s the Difference?
Data science is a rapidly growing field with a wide range of career opportunities. With so many roles available, it can be difficult to understand the differences between them.
This guide provides a clear overview of the responsibilities and skills associated with three of the most popular positions in data science: data scientist, data engineer, and data analyst.
What is data science?
Data science is the application of computer science and statistical analysis to analyze data and extract meaningful insights and information. Data scientists use software tools and algorithms to find patterns and insights in data, test hypotheses and create models and simulations.
They have an overall understanding of the business and work closely with other team members to apply data analysis to solve specific business problems. Data scientists and data engineers collaborate to create and implement data analytics solutions throughout the data analytics process.
Data science is an interdisciplinary field, meaning it combines aspects of different fields such as computer science, statistics, data engineering, and applied mathematics. Due to the wide variety of skills required, hiring managers often use data science as an umbrella term to describe the work of data analysts, data engineers, and others who work with data.
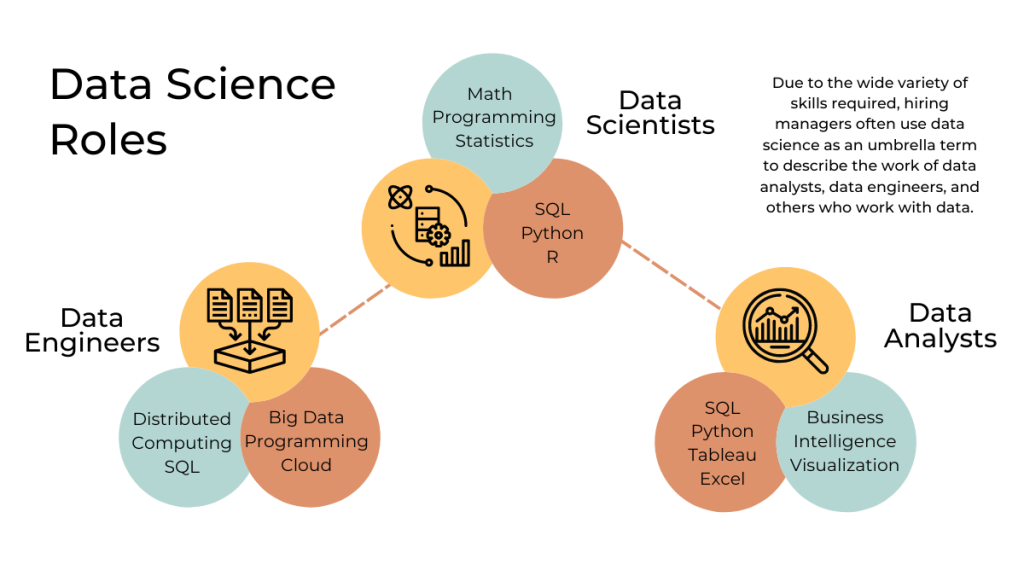
Data Scientist

Data scientists are responsible for analyzing data and using machine learning algorithms to create models and simulations to find meaningful insights into the data. They use various tools and technologies to ingest, store, clean, transform and analyze data to create value for the business.
They have a strong background in statistics and some have undergraduate or graduate degrees in computer science, mathematics, or statistics. Additionally, data scientists have strong communication skills, are creative and curious, and enjoy solving complex problems.
Data Engineer
Data engineers are another type of data science specialization, which is responsible for designing and implementing data storage and processing systems. They identify and solve issues with data storage, ingestion, cleaning, and transformation systems to create value for the business. They work closely with data scientists who use the infrastructure created by data engineers to analyze the data.
Data engineers have a strong background in computer science and have completed coursework in software engineering, distributed systems, and data structures. They have strong communication skills, are creative and curious, and enjoy solving complex problems.
Data Analyst
Data analysts are responsible for identifying, cleaning, and transforming data to create value for the business. They do not have the same level of technical skills as data scientists or data engineers, but they do work with data to create a usable and valuable information product.
Data analysts often have a degree in computer science, statistics, or business administration and have technical skills in data cleaning and data transformation. Data analysts have strong communication skills, are creative and curious, and have a knack for finding insights into data.
Education and Training Requirements
In general, data science roles require a minimum of a bachelor’s degree in computer science, mathematics, statistics, or a related field. Data engineers have a more in-depth technical background than data analysts so it’s recommended to have a degree in computer science.
Data scientists have a more varied educational background. A statistics degree is typical, but some data scientists have degrees in other fields and bring other analytical skill sets to the role. Data scientists should also have a firm grasp of computer science concepts such as data storage, transformation, and analysis.
Many data science roles also require experience working with the programming languages and tools used for data analysis. Companies hiring data scientists may also ask for evidence of additional training.
Benefits of Working in Data Science
Here are some of the major benefits of working in data science:
Conclusion
As data science becomes more important to businesses, there will be more career opportunities for data scientists, data engineers, and data analysts.
If you know the difference between the data science roles, it will help you determine which role is the best fit for your interests and experience. Plus, it will provide insight into the knowledge and training required for each role.
With this information, you can make an informed decision about which career path to take on your journey to becoming a data professional.

Related Data Engineering
ETL Explained: What Is Extract, Transform and Load (ETL) Process?
The Data Engineering Toolkit: What Tools Do Data Engineers Use?
How I Became a Data Engineer: A Guide To The Journey
The Dark Side of Data Engineering: 19 Things To Hate
The Basics of Data Pipelines: What You Need to Know
The Data Engineer Role: What They Do and How to Get Started
Demystifying the Data Science Roles
How To Become A Data Architect: Skills and Responsibilities