SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS – What’s the Difference?

SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS – What’s the Difference?
Understanding the difference between Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) is key to choosing the right cloud service for your business.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explain the differences between these three popular cloud services and how they can help you scale your business.
We’ll also discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each service and provide tips on how to choose the right one for your needs. So if you’re looking to learn more about SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, then this guide is for you!
Types of Cloud Computing [Infographic]
First, here is an infographic that quickly outlines the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and Saas for who manages what. At quick glance, you can see how Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) manages the most compared to if you were to manage on-premise.
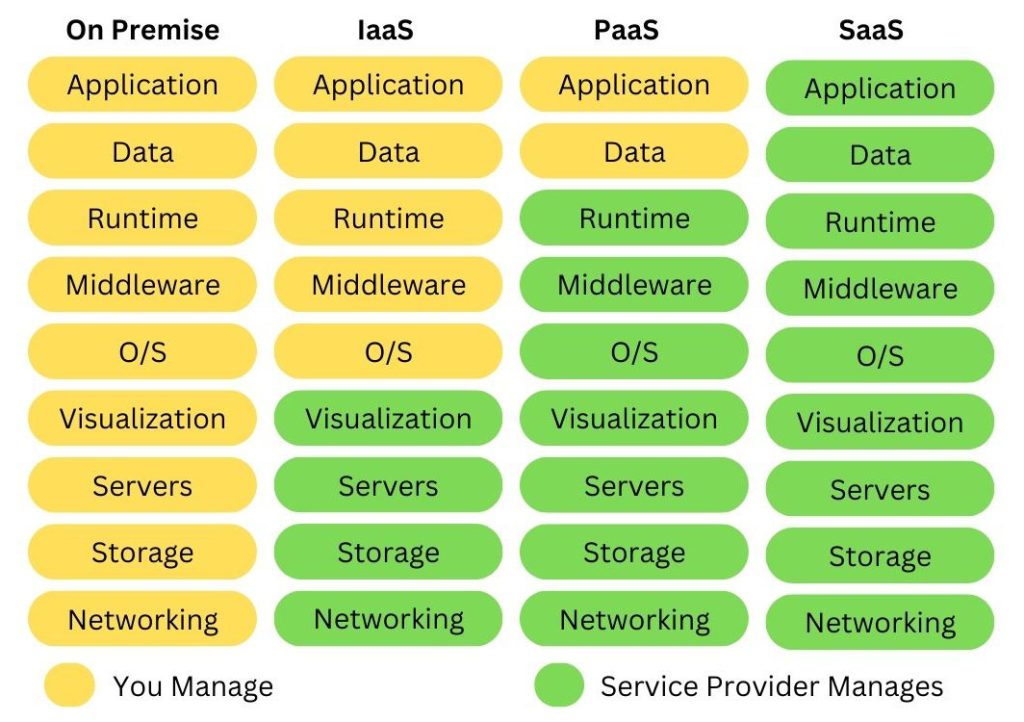
Table Comparison: SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS
Here’s a comparison table between Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
| Aspect | SaaS | PaaS | IaaS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivers software applications via the internet, hosted and maintained by a third-party provider. | Provides a platform that includes development tools, runtime environments, and services for building, deploying, and managing applications. | Offers virtualized computing resources over the internet, including servers, storage, and networking. |
| User Focus | End-users benefit from ready-to-use applications without managing infrastructure. | Developers focus on application development and deployment without managing underlying infrastructure. | IT administrators have control over virtualized infrastructure while managing their own applications and services. |
| Control | Minimal control over software configuration, updates, and infrastructure. | More control over application development and deployment, but less control over underlying infrastructure. | Full control over infrastructure configuration, including OS, runtime, storage, and networking. |
| Scalability | Limited control over scalability as it’s managed by the provider. | Offers some scalability options based on the platform’s capabilities. | Offers flexible scalability with the ability to adjust resources up or down as needed. |
| Maintenance | Provider handles maintenance, updates, and security patches. | Platform and infrastructure maintenance is shared between the provider and the user. | Users are responsible for managing and maintaining the infrastructure, including updates and security. |
| Development | No development or coding required by users; applications are pre-built and hosted. | Focuses on application development and deployment using the provided platform services. | Users are responsible for building, deploying, and managing applications using the provided infrastructure. |
| Examples | Google Workspace, Salesforce, Microsoft 365. | Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Service. | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP). |
| Use Cases | Well-suited for end-users who want easy access to software applications. | Ideal for developers who want to focus on coding and deploying applications without managing infrastructure. | Ideal for IT administrators and developers who need full control over the underlying infrastructure. |
| Cost Model | Typically based on a subscription or usage-based model. | Usage-based pricing model, often factoring in platform resources and services used. | Usage-based pricing model, charging for compute, storage, and networking resources used. |
| Customization | Limited customization options as software is pre-built and hosted. | Customization options within the platform’s constraints and available services. | Full customization of virtualized infrastructure, including operating systems and applications. |
| Example Providers | Salesforce, Google Workspace, Microsoft 365. | Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure, Heroku. | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP). |
What is SaaS?

Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing model in which a provider hosts applications and makes them available to customers over the internet. SaaS applications are typically accessed through a web browser, while the underlying software and data are stored on the provider’s servers. This eliminates the need for customers to install and run applications on their own computers or in their own data centers.
SaaS applications are often sold on a subscription basis, with users paying a monthly or annual fee. This allows companies to use the latest version of an application without having to worry about managing its installation or upgrading it over time. Organizations can also take advantage of SaaS to quickly roll out new applications without a large upfront investment in infrastructure or IT staff.
The SaaS model is gaining popularity due to its scalability and convenience. Companies can access sophisticated software without having to invest heavily in hardware and IT staff. Additionally, they can scale up or down their usage based on their needs, and they don’t have to worry about maintaining or upgrading applications.
Some examples of SaaS include:
What is PaaS?

Platform as a Service (PaaS) is an integrated computing platform that provides users with a platform to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexities of creating and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an application. Additionally, PaaS often includes features such as scalability, monitoring, backup, and recovery.
PaaS typically includes an operating system, programming language execution environment, database, web server, and various other services. This allows developers to focus on the development of the application, rather than worrying about the underlying infrastructure. By using PaaS, developers can quickly launch applications into the cloud, with minimal configuration and setup required. PaaS also offers a range of other benefits, such as cost savings, faster deployment times, and fewer operational headaches.
By using PaaS, organizations can reduce their IT overhead, as they no longer need to maintain and manage the physical hardware and software required for application development. In addition, PaaS can be used to quickly deploy new applications or make changes to existing ones, allowing organizations to stay agile and competitive in their respective markets.
Some examples of PaaS include:
What is IaaS?

Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model in which an organization outsources the physical infrastructure of its IT systems and services to a third-party provider. This provider offers virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, networking, and operating systems over the internet. IaaS is different in that it provides the underlying foundation of a system, while the other two models provide platforms and software applications.
For organizations that are looking to move away from expensive hardware and on-premise solutions, IaaS can be a great option. It allows businesses to pay only for the infrastructure they need, when they need it, and scale up or down quickly in response to changing needs. Since the service provider manages the hardware, businesses don’t need to invest in expensive IT personnel and equipment to maintain their systems. IaaS also provides increased flexibility, reliability, and scalability when compared to traditional on-premise solutions.
Overall, Infrastructure as a Service is a cost-effective and flexible way for companies to meet their IT infrastructure needs. With the help of a third-party provider, businesses can access the computing resources they need without the need for expensive hardware and personnel. This allows them to focus more of their resources on developing innovative solutions to solve their unique business problems.
Some examples of IaaS include:
Conclusion
SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are all types of cloud computing that are growing in popularity among businesses. Understanding the difference between these popular cloud services is the first step towards choosing the right cloud computing service for your business.
SaaS delivers applications via the internet, while PaaS provides businesses with a software development environment. IaaS provides customers with the infrastructure they need to run their applications.
SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS each come with their own set of benefits and drawbacks. When selecting the right service for your business, it’s important to understand your business needs, your IT needs, and your financial needs. From there, you can select the right service for your needs.

Related Cloud Computing
What Is a Cloud Engineer?
A Gentle Introduction to Cloud Computing
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS – What’s the Difference?
3 Must-Have Skills for a Cloud Computing Career