GIS and Big Data: Challenges and Opportunities

With the advent of big data, GIS has become an essential tool for managing and analyzing spatial data. This article will explore the different ways in which users are integrating Big Data in GIS. For example, this includes real-time data analysis, spatial data mining, location-based services, predictive analytics, image analysis, and social network analysis.
How is Big Data Connected to GIS?
Professionals are increasingly leveraging Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to process, analyze and visualize large amounts of data known as big data. Big data refers to the massive amount of structured and unstructured data. It can be generated from various sources such as sensors, social media, and satellite imagery.
This data can be used to gain valuable insights into trends and patterns, which can inform decision-making. For example, fields such as urban planning, disaster management, and environmental monitoring can leverage big data.
What Are Examples of GIS and Big Data?
The integration of big data with GIS provides new opportunities for extracting valuable insights from complex spatial datasets. Here are some examples of how big data is used in GIS:
- Real-time Data Analysis: GIS integrates real-time data from various sources. For instance, this includes sensors, social media, and weather forecasts to gain insights into current trends and conditions.
- Spatial Data Mining: GIS can help in discovering hidden patterns and trends within spatial data. Machine learning algorithms and geostatistical techniques are two common ways.
- Location-based Services: GIS can provide location-based services such as routing, navigation, and geofencing, which are enabled by big data.
- Predictive Analytics: GIS can make predictions based on past trends and future projections of big data for decision-making.
- Image Analysis: GIS can process and analyze high-resolution images from satellites and drones. In turn, this can monitor changes in the environment and infrastructure.
- Social Network Analysis: GIS can analyze social networks and identify patterns of interactions and behavior for urban planning and disaster response.
Big Data Geospatial Software
Esri is pioneering the usage of Big Data in GIS through various analytical solutions. This includes:
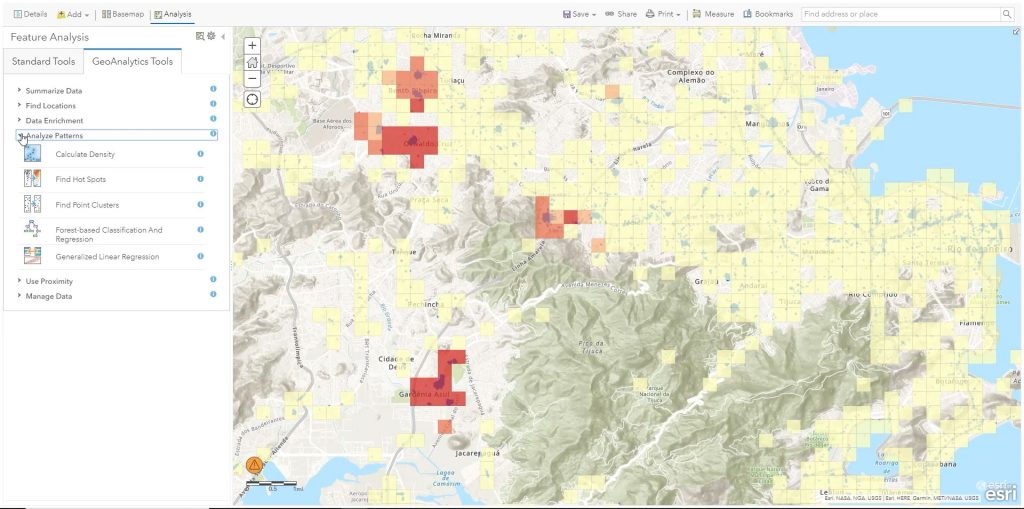
ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Engine – The ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Engine is a tool for performing geospatial analysis wherever your big data is stored. From a data lake to a data warehouse or in ArcGIS, you’ll be able to process and analyze large volumes of spatial data. Finally, you’ll be able to gain insights into complex spatial patterns such as hot spots, regression, and clustering.
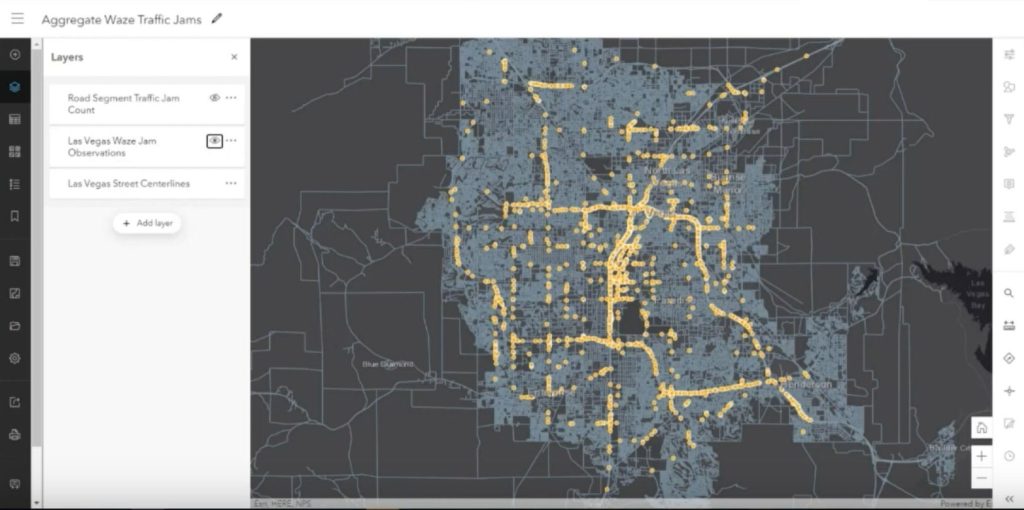
ArcGIS Velocity – This big data solution allows you to ingest data from the Internet of Things (IoT) through ArcGIS Online. From there, you can perform real-time analysis of location-based streaming data.
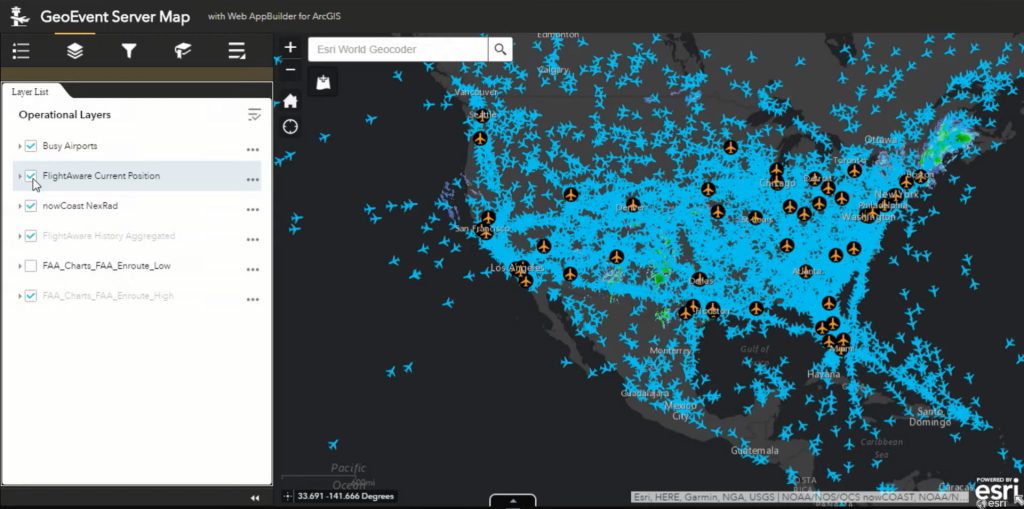
ArcGIS GeoEvent Server – ArcGIS GeoEvent Server is a real-time event processing engine for better situational awareness. It enables organizations to collect, process, and analyze real-time data streams from various sources such as sensors, IoT devices, social media, and other business systems. It can also integrate with other ArcGIS products, including ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Enterprise, to enable users to visualize and analyze real-time data in maps, dashboards, and reports.
Conclusion
The integration of big data with GIS provides new opportunities for extracting valuable insights from spatial datasets. Overall, this can enable better decision-making and more efficient resource management.
In this context, the use of GIS and big data is becoming increasingly important for organizations and governments seeking to make data-driven decisions to address complex spatial challenges.
Want to learn more about GIS? Check out our articles on GIS software, vector and raster data, and types of GIS formats.
