What Is Geographic Information Systems (GIS)?

Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a technology-based system that captures, stores, analyzes, and visualizes geographical data.
Over the years, GIS has become a game-changer to help users understand the relationships, patterns, and trends between geographic locations and features.
Plus, it enables users to create maps, visualize data, analyze and interpret patterns, and make informed decisions based on spatial data.
Applications of GIS and Geospatial Data
We use GIS (Geographic Information Systems) in a wide variety of applications across many industries. Here are some of the prime examples:
- Urban Planning: GIS systems can model and analyze urban land use, transportation, and infrastructure. This helps planners to make informed decisions about development and growth.
- Environmental Management: GIS can help to monitor and manage natural resources, track species’ habitats, and predict the effects of climate change.
- Emergency Management: GIS can help to manage and respond to natural disasters, disease outbreaks, and other emergencies.
- Transportation: GIS can help to optimize routes for transportation networks, analyze traffic patterns, and track vehicles and assets.
- Public Health: GIS can be used to track disease outbreaks, analyze health trends, and manage healthcare resources.
- Marketing and Sales: GIS can help businesses to target their marketing efforts by analyzing demographic data and consumer behavior patterns.
- Agriculture: GIS can be used to optimize crop yields, manage land use, and monitor soil and water quality.
- Energy Management: GIS can help to manage and optimize energy distribution networks, monitor energy usage, and identify opportunities for energy conservation.
GIS has a wide range of applications across many industries. Overall, it can help us improve decision-making processes and optimize operations by providing a better understanding of spatial data.
Types of GIS Data
Geospatial data can come in various GIS formats such as satellite imagery, aerial photography, GPS, and surveys. But vector data and raster data are the two most common types of formats for representing spatial information.
Vector Data
Vector data represents spatial features using points, lines, and polygons. Each of these features has specific geographic coordinates that define its location.
Vector data is typically used to represent discrete objects or features that have clear boundaries, such as roads, buildings, and administrative boundaries. Vector data is also useful for performing spatial analyses that involve measuring distances, areas, or other geometric properties of features.
Raster Data
On the other hand, raster data represents spatial features using a grid of cells or pixels. For raster data, each cell represents a small area of the earth’s surface. Cells are assigned a value that represents a particular attribute, such as elevation, temperature, or land cover type.
Raster data is typically used to represent continuous phenomena that vary over space, such as elevation, temperature, or rainfall. Raster data is also useful for performing spatial analyses that involve mathematical operations. For instance, this includes processes such as interpolation, surface analysis, or terrain modeling.
Both vector and raster data have their unique strengths and weaknesses. But the choice between the two formats depends on the specific needs of the GIS application.
Popular GIS Software
GIS software offers a variety of tools and capabilities to manipulate and analyze spatial data. Some of the key features of GIS software include data management, spatial analysis, mapping and visualization, and network analysis.
There are several popular mapping platforms available, and their popularity varies depending on the industry, purpose, and user community. Here are some of the most commonly used GIS software:
- ArcGIS by ESRI: ArcGIS is one of the most popular and widely used GIS software for mapping and spatial analysis. It is used by governments, businesses, and organizations for managing and analyzing spatial data.
- QGIS: QGIS is a free and open-source GIS software that allows users to create, edit, visualize, analyze, and manage geospatial information.
- Google Earth: Google Earth is a web and desktop-based GIS software that enables users to explore the world. Additionally, you can create custom maps, and perform basic spatial analysis using 3D imagery and satellite data.
- GRASS GIS: GRASS GIS is a free and open-source GIS software for geospatial data management, analysis, and visualization. It is often used by researchers, government agencies, and NGOs.
- MapInfo Pro: MapInfo Pro is a desktop-based GIS software that provides tools for mapping, spatial analysis, and data visualization. It is widely used by businesses and organizations for location-based decision-making.
- Global Mapper: Global Mapper is a desktop-based GIS software that provides tools for mapping, terrain analysis, and 3D modeling. It is used by government agencies, surveyors, and geospatial professionals.
- FME (Feature Manipulation Engine): FME is a data integration software developed by Safe Software. This software allows users to manipulate, transform, and convert geospatial and non-geospatial data from various formats and sources. It can handle a wide range of data formats including CAD, GIS, BIM, database, cloud-based, and web-based formats, among others.
These are just a few examples of the most popular GIS software. The choice of GIS software largely depends on the user’s needs, budget, and technical skills.
Geospatial Analysis and Modeling
GIS can help organizations to better understand the geographic distribution of their data. But the main way to identify trends and patterns and make predictions is through geospatial analysis.
Here are some of the top geoprocessing tools to help manipulate data:
- Buffer: The buffer tool creates a zone around a feature by calculating a distance or area around it.
- Clip: The clip tool allows you to create a new feature layer by clipping an existing layer to the boundary of another feature layer.
- Merge: The merge tool combines two or more feature layers into a single layer.
- Intersect: The intersect tool creates a new feature layer by overlapping features from two or more input layers.
- Union: The union tool creates a new feature layer by combining features from two or more input layers.
- Spatial Join: The spatial join tool allows you to join attributes from one layer to another based on their spatial relationship.
- Dissolve: The dissolve tool combines features within a single layer that share a common attribute value.
- Project: The project tool allows you to reproject a layer from one coordinate system to another.
- Calculate Field: The calculate field tool allows you to perform calculations on the attributes of a feature layer and create a new field with the results.
These are just a few examples of the many geoprocessing tools available. The choice of tool often depends on the specific requirements of the analysis and the type of spatial data being processed.
The Rise of Online Web Mapping
Online mapping has become an integral part of our daily lives, with the ability to access maps and location-based information through the internet. It’s GIS that powers these types of maps. The rise of online mapping can be attributed to a number of factors. For example, this includes advancements in technology, the availability of data, and the increasing demand for location-based services.
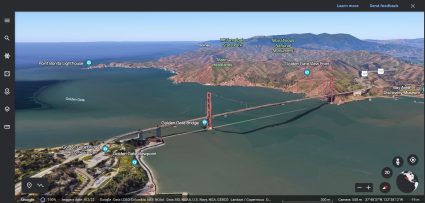
One of the key drivers of the rise of online mapping is the advancement in technology, specifically in web-based mapping applications. It’s now possible to create dynamic and interactive maps that can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This allowed for the development of mapping platforms such as Google Maps, Bing Maps, and OpenStreetMap, which are now widely used for navigation, route planning, and location-based search.
Another factor that has contributed to the rise of online mapping is the availability of data. With the increasing amount of geospatial data available from sources such as satellite imagery, GPS, and crowdsourcing, it has become possible to create detailed and accurate maps for a variety of applications. This data can now be easily accessed and incorporated into online mapping platforms for public use.
What Are the Trends in GIS?
GIS technology is constantly evolving, driven by new developments in data acquisition, processing, and visualization. Here are some of the current trends in GIS:
Cloud-based GIS: Cloud-based GIS services allow users to store, process, and access geospatial data in a highly scalable and cost-effective manner. Cloud-based GIS platforms such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure are becoming increasingly popular, offering flexible computing resources and easy access to a wide range of geospatial data.
Big Data and AI: The explosion of big data in GIS and the increasing availability of AI and machine learning tools are transforming the way we analyze and visualize geospatial data. These technologies are helping to unlock insights from vast amounts of geospatial data. This has led to new applications in areas such as predictive modeling, real-time monitoring, and precision agriculture.
3D GIS: With the increasing availability of 3D data and visualization tools, 3D GIS is becoming an important trend in GIS. 3D GIS enables users to visualize and analyze data in a more realistic and immersive perspective.

Mobile GIS: With the increasing use of smartphones and tablets, mobile GIS is becoming more important. Mobile GIS enables users to access and interact with geospatial data from anywhere, using mobile devices. This is leading to new applications in areas such as field data collection, asset management, and emergency response.
Open data and open source GIS: Open data and open source GIS software are becoming more widely used, providing access to a wealth of geospatial data and tools at little or no cost. Open source GIS software such as QGIS, GRASS GIS, and GeoServer is becoming more popular, offering a range of powerful tools for geospatial analysis.
These trends in GIS are shaping the future of geospatial analysis, enabling us to better understand and manage our world
Conclusion
In conclusion, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have become an integral part of various industries, including government, businesses, and non-profit organizations. GIS software enables users to collect, store, manage, analyze, and visualize spatial data, providing valuable insights into the world around us.
With the continued development and advancements in GIS technology, we can expect to see even more innovative and sophisticated applications in the future. Whether you are a scientist, planner, or business owner, GIS can help you make informed decisions and solve complex problems.
As our world becomes increasingly interconnected and data-driven, GIS will continue to play a critical role in shaping our future. What do you think? Please let us know in the comment section below.


