The Basics of Data Pipelines: What You Need to Know
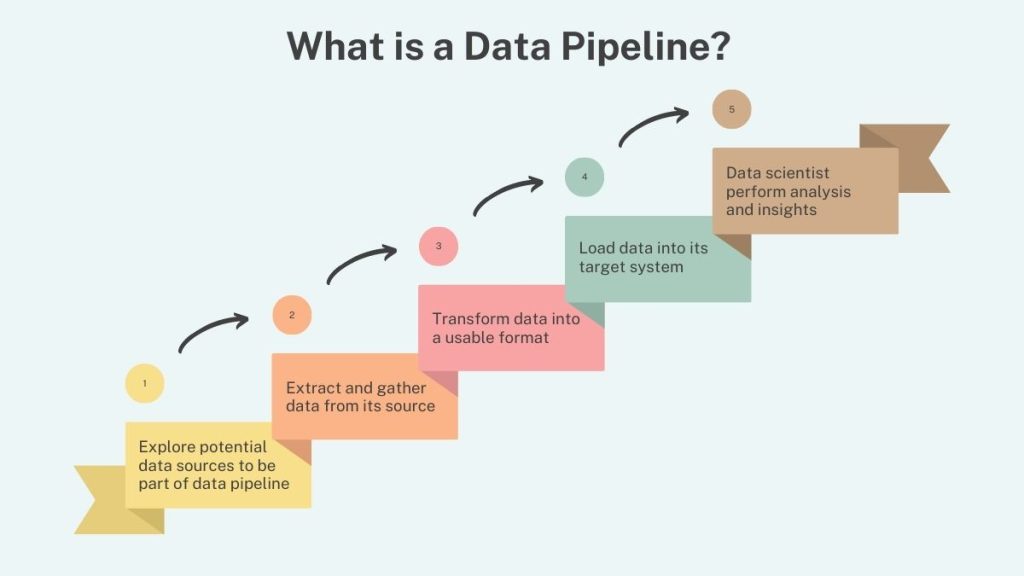
What is a data pipeline?
Data pipelines are the backbone of modern data-driven operations. They enable organizations to collect, transform, and analyze their data quickly and accurately. As more businesses become digital, the need for efficient data pipelines becomes even more critical.
This article will provide an overview of the basics of data pipelines – what they are, what they can do, and how they work. We will also discuss the various components that make up a data pipeline, such as data sources, processing systems, and data storage solutions. With this knowledge, you’ll be able to determine the right data pipeline setup for your business.
The basics of a data pipeline
A data pipeline is a sequence of data processing systems that transport data from one source to another. It follows a predefined workflow, which makes it easier to integrate with other systems, such as visualization tools. It also helps businesses to save time and money by reducing manual processes and optimizing the use of resources.
Here are some of the common components of a data pipeline:
Benefits of data pipelines
There are a plethora of benefits to using data pipelines in an organization. Here are some of the major reasons why you might want to implement one:
Data pipeline tools
As part of the ETL process (Extract, Transform, Load), here are some of the primary tools of a data pipeline:
Big data and data pipelines
With so many businesses using big data, there is an increased need for data pipelines. Traditionally, data pipelines have been used to process smaller amounts of data. With the recent rise of big data, data engineers have had to start building data pipelines that can handle much larger amounts.
This has led to important changes in the way data pipelines are designed and implemented. Data engineers now have to ensure that the data is distributed across multiple nodes in the system, data is processed asynchronously, and the system is scalable. This means that big data and data pipelines go hand in hand.
Big data, distributed systems, and data pipelines make it easier for organizations to collect, transform, and analyze their data quickly and accurately. This, in turn, enables them to make better business decisions. With a large amount of data from a variety of sources, businesses need robust and scalable data pipelines to manage and process it.
How data engineers use data pipelines
Data engineers use a variety of tools to build data pipelines. These tools include ETL tools, a data warehouse, and an event data platform. Data engineers first determine where the data comes from and where it needs to go. They then create a diagram that shows how the data flows through the data pipeline. Finally, they integrate the data sources and data destinations to build the data pipeline.
Data engineers use data pipelines to transform data and integrate it across different systems. Data engineers use data warehouses to store large amounts of raw data, such as sales and inventory data. They then use ETL tools to transform the data and load it into a data lake. An event data platform collects different types of event data and sends it to a data lake. Data engineers then use the data in the data lake to load it into the data warehouse.
Data engineers can also use data pipelines to enrich data and share it across different systems. For example, they can use a data lake to collect customer information and then distribute it to other systems, such as databases, data warehouses, visualization tools, and artificial intelligence systems. This is the stage where data scientists, AI engineers, and business analysts make sense of the data and turn it into action.
Conclusion
In data engineering, data pipelines provide all the legwork for data collection and processing. They allow organizations to collect data without the need for human intervention. This is a good thing because it can also reduce errors and increase the efficiency of operations in an organization.
The benefits of data pipelines are many, including consistency, flexibility, accuracy, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. There are various components that make up a data pipeline, including data sources, data stores, data transformation, and data destinations. Data engineers use these components to build robust and scalable data pipelines that can handle large amounts of data.
Data pipelines are central to the success of businesses that rely on data, such as marketing companies, online retailers, and financial institutions. With this knowledge, you’ll be able to determine the right data pipeline setup for your business.

Related Data Engineering
The Basics of Data Pipelines: What You Need to Know
The Dark Side of Data Engineering: 19 Things To Hate
The Data Engineering Toolkit: What Tools Do Data Engineers Use?
How To Become A Data Architect: Skills and Responsibilities
Demystifying the Data Science Roles
ETL Explained: What Is Extract, Transform and Load (ETL) Process?
An Introduction to Data Engineering: The What, Why and How
The Data Engineer Role: What They Do and How to Get Started